Risk of sea level rise in the Euro–Med region & a new web app to support climate action
 Extreme sea levels are projected to increase significantly along Europe's coasts by 2100. The findings from a new study indicate that global warming could cause extreme sea levels to increase significantly. Massive coastal flooding in northern Europe, which now occurs once every century, could happen every year if greenhouse gas emissions continue to rise. The Mediterranean coast could see these 100-year extreme sea level events even several times a year. The increase in frequency of these exceptional events will likely push existing coastal protection structures beyond their design limits, leaving a large part of coastal zones exposed to flooding. Under high-end warming, 5 million Europeans, currently under threat of a 100-year coastal flood event, could be at risk from coastal flooding every year by the end of this century.
Extreme sea levels are projected to increase significantly along Europe's coasts by 2100. The findings from a new study indicate that global warming could cause extreme sea levels to increase significantly. Massive coastal flooding in northern Europe, which now occurs once every century, could happen every year if greenhouse gas emissions continue to rise. The Mediterranean coast could see these 100-year extreme sea level events even several times a year. The increase in frequency of these exceptional events will likely push existing coastal protection structures beyond their design limits, leaving a large part of coastal zones exposed to flooding. Under high-end warming, 5 million Europeans, currently under threat of a 100-year coastal flood event, could be at risk from coastal flooding every year by the end of this century.
In the Mediterranean, new evidence indicates that sea level has risen by about 30cm in the last 1,000 years. Researchers, from Italy's National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, have just published results of a study attributing an acceleration in sea level rise to global warming, despite the uncertainties associated with the chronology on sea level change occurring during the last millennia. The study investigated a number of millstones quarries, using data from the remnants of the ancient quarries and assessing the intervening sea level change since the quarries were abandoned.
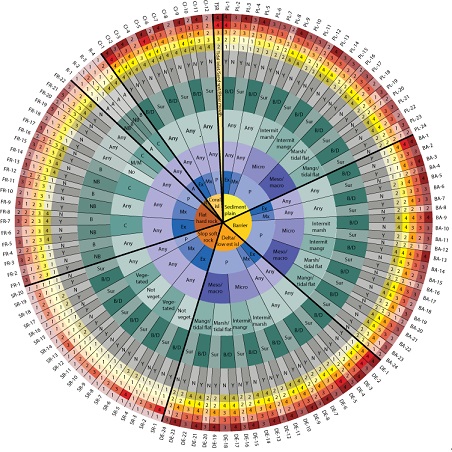
To boost adaptation action for the 1 billion people living in coastal areas worldwide, a web app has newly been released. The Coastal Hazard Wheel can be used to consider how different coastlines should respond. An infographic assists in areas with less data, by helping users classify their location using information about local geology, tides and hazards such as flooding and erosion. Bridging the gap between scientists, policy-makers and the general public, the web app launched by the United Nations Environment Programmme (UNEP),will support people living and working on coasts in making decisions on how to adapt to a changing climate. It opens up access to scientific background material and coastal classification data, in order to aid decision-making and standardise its communication worldwide.
Resources: Web App | UNEP Guide for coastal stakeholders: Quick Start – Main Manual – Management Hazard Options