Morocco launches Argan oil project to mitigate climate change
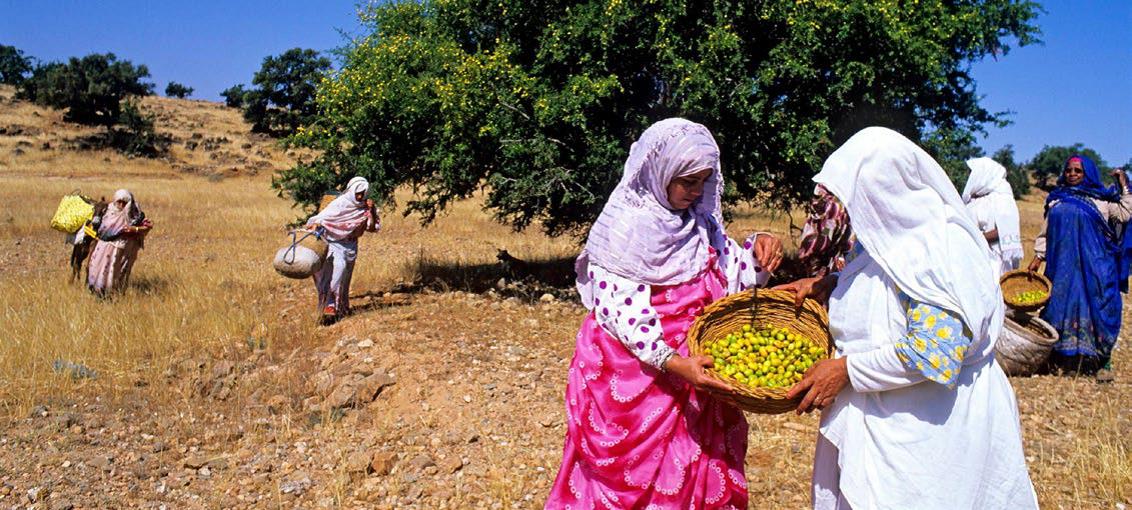

A Moroccan Nationally Appropriate Mitigation Action (NAMA), based on Argan oil production has been granted USD 39.3 million of funding by the Green Climate Fund (GCF). Through this ambitious project, the Moroccan Government aims at the Development of Argan Orchards in Degraded Environments in the south of the country. Modern techniques will be introduced to raise production levels of Argan oil in a sustainable way, thus reducing anthropogenic and industrial pressure on wild Argan forests, along with the rehabilitation of degraded areas for Argan oil production.
The Moroccan government sees the current high demand for Argan oil on international markets as an opportunity to tie climate change targets to its sustainable development goals. Argan oil has long been one of the source of livelihoods for Morocco’s Berber population. Smallholders in the region traditionally relied on a sylvo-pastoral approach drawing on the synergies between forests and grazing of livestock. While Argan forests still cover around 820,000 hectares, one-third of the original tree cover has already been lost due to pressures from charcoal production and unsustainable agricultural practices.
The advance of desertification into the Argan orchard areas increasingly threatens the livelihoods of local communities. Argan trees are a true bastion against desertification. At maturity, Argan trees (Argania spinosa), may reach 10 meters in height and individuals may live for 200 years. By boring deep into the ground, they play a key role in halting soil erosion. The tree also has an amazing ability to adapt to severe droughts by simply going dormant until it can sense moisture once again.
The NAMA was developed in cooperation with UNDP’s Low Emission Capacity Building Programme through the support of the European Commission, Germany’s Federal Ministry for the Environment, and the Australian government.