Improving Climate Information for Adaptation
 The ClimaSouth Seminar "Improving Climate Information" was held 28-30 April, 2014 in Lecce, Italy. The seminar framed the opportunities and challenges in the region for enhancing climate information in order to improve vulnerability assessments and adaptation.
The ClimaSouth Seminar "Improving Climate Information" was held 28-30 April, 2014 in Lecce, Italy. The seminar framed the opportunities and challenges in the region for enhancing climate information in order to improve vulnerability assessments and adaptation.
An overview of the material that was presented at the seminar, and a summary of seminar discussions, are contained in the Seminar Handbook
Some of the issues from the workshop are expanded upon below.
Building from information by the IPCC:
In 2013, the IPCC published its latest review of the Physical Basis of Climate Change (Working Group I, WGI ). The Summary for Policymakers provides an overview. The main message for the ClimaSouth region is projected warming trends that are greater than the global mean, and general downward trends in precipitation, but which vary by season. While some further details of expected trends in features such as extreme weather events are discussed in the full report, the need for downscaling of information to inform adaptation is returned to below.
In 2014, the IPCC published its latest review of Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability (Working Group II, WGII ). The Summary for Policymakers provides an overview.
Videos were presented at the Lecce seminar, produced by CMCC / FEEM / ICCG (Italy) summarising the above two IPCC reports with a Mediterranean perspective:
WG1 video Physical Basis of Climate Change, explained climate experts: C. Carraro ( ICCG/ FEEM/ CMCC ), Vice-Chair of the Working Group III and Member of the Bureau of the IPCC; Carlo Barbante (Institute for the Dynamics of Environmental Processes, CNR/University of Venice); Paolo Ruti (ENEA), Contributing Author AR5 WGI; Antonio Navarra ( CMCC ).
WGII video Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. This video explores the contents of the Report narrated by the experts: Sergio Castellari, CMCC - IPCC Focal Point for Italy; Riccardo Valentini, CMCC - IPCC WG2 AR5 Coordinating Leading Author; Francesco Bosello, CMCC - FEEM - IPCC WG2 AR5 Contributing Author. The video is introduced by Jonathan Lynn, IPCC - Head, Communications and Media Relations.
Europe and International Resources and Processes
The seminar was provided with an overview of the European Union Adaptation Strategy and the Climate-ADAPT Tool
A summary of impacts and vulnerability for Europe was published in 2012 by the European Environment Agency: Climate change, impacts and vulnerability in Europe 2012 - An indicator-based report.
Some key impacts of current and projected climate change in the Mediterranean can be summarised:
- Decrease in annual river flow
- Increasing risk of biodiversity loss
- Increasing risk of desertification
- Increasing water demand for agriculture
- Decrease in crop yields
- Increasing risk of forest fire
- Increase in mortality from heat waves
- Expansion of habitats for southern disease vectors
- Decrease in hydropower potential
- Decrease in summer tourism and potential increase in other seasons
Presentations at workshop reported developments on adaptation under the UNFCCC as well as Working with Climate Data in the National Adaptation Plan (NAP) Process
Global Framework for Climate Services
The concept of better managing extreme weather events now as a contribution to longer-term adaption, is increasingly recognised, as evidenced by the IPCC special report on managing extreme weather events (full title: Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation).
This recognition has partly motivated the development in recent years of the Global Framework on Climate Services ( GFCS ). The seminar presentation on GFCS describes the history, and gives early examples of GFCS initiatives.
Examples were presented at the seminar from the German Climate Service Center, which has been experimenting with different products and approaches in the provision of climate services.
Some additional resources that illustrate the proactive way that climate services are now being promoted and developed to stimulate adaptation in society:
The Climate ExChanges book (produced by the World Meteorological Organisation and Tudor Rose), with many examples of climate services in practice, and including an introductory chapter describing How climate services can help people adapt to variability and change.
A major initiative in the agriculture sector is the CGIAR Research Program on Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security (CCAFS), producing a 2014 report on climate services in agriculture: Scaling up climate services for farmers in Africa and Asia
Downscaled Climate Information for Vulnerability Assessment and to Inform Adaptation Actions
One of the limitations of the information from the 2013 IPCC report is spatial resolution. Downscaling is a route to information at appropriate scales to inform adaptation strategies and actions.
Presentations at the seminar reported some of the technical challenges and opportunities in undertaking downscaling of global change scenarios:
Downscaling for actionable information
Downscaling for the Mediterranean
Presentations also provided examples from the ClimaSouth region, either by a ClimaSouth country or undertaken in collaboration with international centres:
Examples were provided of using high resolution (downscaled) scenarios to assess impacts and vulnerability
Downscaled Mediterranean Scenarios and Impact Modelling
Morocco experience with the FAO MOSAIC modelling system for assessing impacts on agriculture
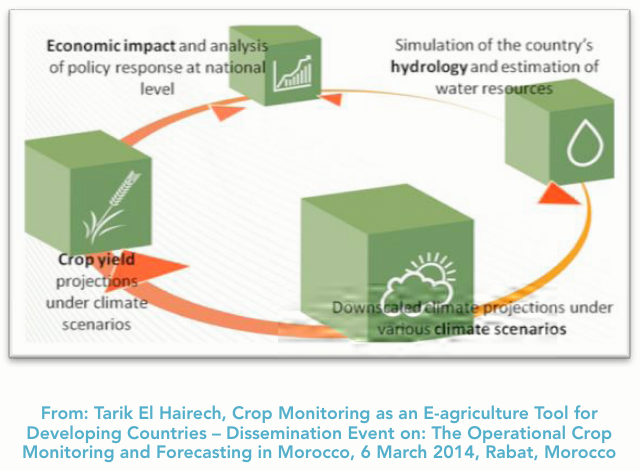 MOSAIC = MOdelling System for Agricultural Impacts of Climate Change
MOSAIC = MOdelling System for Agricultural Impacts of Climate Change
A strong endorsement on the need for enhanced downscaling capacity amongst ClimaSouth countries was a key outcome of the Lecce seminar. Some themes for such capacity development were (i) to recognize the contrasting capacities across ClimaSouth countries, (ii) to recognize the need for downscaling capacity, not just for global change scenarios, but also for early warning systems (monitoring, seasonal forecast), (iii) ensure the connection was made between downscaling capacity and the end goal of enhanced information for vulnerability assessment and adaptation actions (such as described in the above figure describing the MOSAIC concept).